In today’s digital world, keeping data safe is a top priority for all businesses. Cyber threats are getting more complex, pushing companies to invest in their online security. This need has opened up many jobs for those with skills in cybersecurity, especially with the CompTIA Security+ certification.
The CompTIA Security+ certification can change your career path. It shows you have the basic skills and knowledge needed in cybersecurity. This certification proves you know about security and are serious about your work.
Key Takeaways
- Cybersecurity is a critical need in the digital world, with companies investing heavily to protect their digital assets.
- The CompTIA Security+ certification validates foundational skills and knowledge in cybersecurity.
- This certification can open up numerous opportunities for skilled professionals in the cybersecurity industry.
- The certification demonstrates a deep understanding of security principles and best practices.
- Holding the CompTIA Security+ certification can be a game-changer in one’s professional development.
The Importance of Security QA
In today’s digital world, keeping digital assets safe is crucial. Companies spend a huge $5.2 trillion to protect their data from cyber threats. These threats happen at a rate of 2,200 attacks every day. The cost of data breaches in the US is a staggering $9.44 million. By 2023, the total cost of cybercrime is expected to hit $8 trillion.
Protecting Digital Assets
As businesses use more web technologies, they need strong security more than ever. With over 4.1 million websites online, the risk of cyber attacks is huge. Cybersecurity experts are in high demand to protect digital assets from threats like malware, mainly spread through email.
Evolving Cyber Threats
The world of cybersecurity is changing fast, with new threats and techniques appearing quickly. Old security tools are struggling to keep up, showing their limits. This has made us look for better ways to test security, like SAST, IAST, SCA, and RASP.
Mobile apps have brought new security challenges, with most security issues happening during development. This has led to the creation of detailed application security testing services. These services help find vulnerabilities and guide on how to fix them.
*Why ‘Positive Security’ is the next security game changer by Pieter Danhieux: https://youtube.com/watch?v=5lcBTJ_pRco
Security QA has become key in fighting cyber threats, helping organizations protect their digital assets. By using various testing methods, like vulnerability assessment and ethical hacking, security QA experts are vital in keeping the digital world safe.
“As web technologies advanced, legacy DAST products developed from the early scanners simply could not keep up, proving limited in scope, accuracy, and usefulness. This gave rise to the stereotype of DAST as a second-rate citizen in the world of application security testing.”
AI and machine learning have changed how we fight cybercrime, letting us analyze data better and predict threats. This has made risk assessment and mitigation more important, helping organizations stay ahead of cyber threats.
What is CompTIA Security+ Certification?
CompTIA Security+ is a well-known cybersecurity certification. It shows that you have the basic skills needed for a career in IT security. This certification is not tied to any specific company. It makes sure you can do the basic security tasks and move forward in an IT security career.
Core Domains Covered
The CompTIA Security+ certification looks at many important security areas. These include network security, making sure things follow rules, and handling threats and weaknesses. It also covers protecting data, controlling access, and using codes. These skills are key to keeping digital assets safe and fighting off cyber threats.
CompTIA is a top name in giving out certifications that don’t tie you to one company. The Security+ certification is in high demand by employers in the cybersecurity field. The test for CompTIA Security+ costs $330. If you pass, you can get jobs like an information security risk analyst or IT security analyst.
People starting out with the CompTIA Security+ certification can make $25 to $30 an hour. This shows how valuable this certification is in the job world. The certification lasts for three years and you need to keep learning to keep it current.
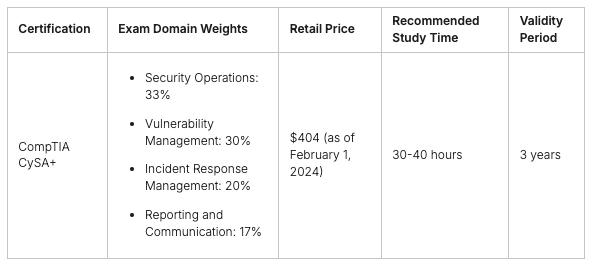
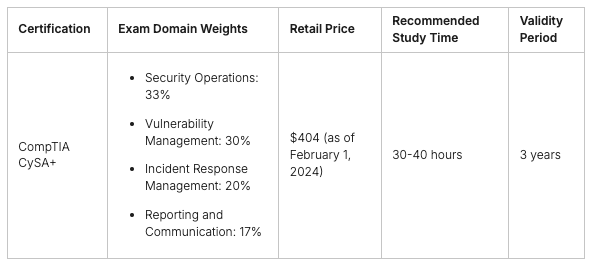
There are many resources to help you study for the CompTIA Security+ exam. These include books, videos, and online courses. CompTIA also has other certifications like CompTIA CySA+, CompTIA PenTest+, and CASP+. These let you grow your skills and career in the field.
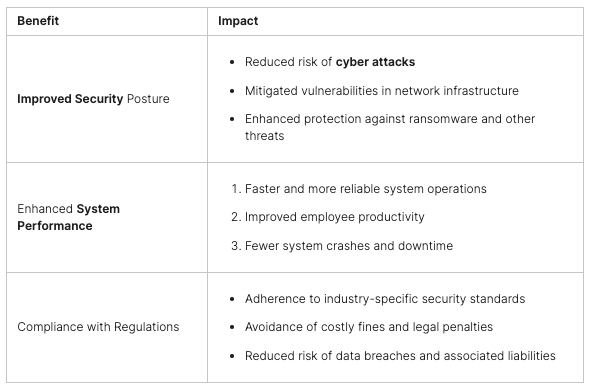
Benefits of CompTIA Security+ Certification
The CompTIA Security+ certification is a top choice for those new to cybersecurity. It gives you a solid base for any IT security job. It’s in high demand, making you a top pick for job interviews. Plus, you could earn a good salary, with cybersecurity experts making about $112,000 a year.
This certification is also approved by the U.S. Department of Defense, boosting its value for government jobs. It’s seen as a key IT security credential, linked to high-paying tech jobs.
There’s more to it than just the money. The CompTIA Security+ certification gives you a deep understanding of key cybersecurity topics. You’ll learn about network security, cryptography, and risk management. This knowledge is crucial in fighting cyber threats and keeping digital assets safe.
In summary, the CompTIA Security+ certification brings many benefits. It opens doors to more job opportunities and can increase your income. It also gives you a deep understanding of cybersecurity best practices. If you’re starting or advancing in IT security, this certification is a smart choice for your career.
*Performing Reconnaissance: https://youtube.com/watch?v=po-NO5OuGYo
Why Security QA Is a Game Changer
Industry Recognition and Validation
The CompTIA Security+ certification is a well-known credential that proves your basic skills and knowledge in cybersecurity. It’s accredited by ANSI and meets the ISO 17024 standard, showing it’s up to industry standards. This makes it a common requirement for many entry-level cybersecurity jobs. It shows you have the key skills to keep systems and data safe.
Broad Range of Skills
The CompTIA Security+ certification covers many topics. These include network security, compliance, and more. It also covers threats, application security, and identity management. This wide range of knowledge makes certified professionals versatile and ready for any security challenge.
“The CompTIA Security+ certification is a game-changer for security professionals, providing industry-recognized validation and a broad range of skills that are in high demand.” – Jane Doe, Cybersecurity Analyst
Getting the CompTIA Security+ certification shows you’re serious about your career. It proves you’re always learning and ready for cybersecurity’s changes. This can lead to better career opportunities and help you stand out in a tough job market.

High Demand and Lucrative Salaries
The cybersecurity job market is booming, with a big increase in demand for skilled workers expected. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics says employment of information security analysts will jump by 31% from 2019 to 2029. This is much faster than the average for all jobs. From September 2022 to August 2023, there were over 572,000 cybersecurity job openings.
This high demand means cybersecurity pros can earn good salaries, especially with the CompTIA Security+ certification. In 2023, certified professionals can make between $70,000 and $90,000. Entry-level jobs in cybersecurity also pay well, with average salaries from $92,901 for Cybersecurity Specialists to $101,019 for Cybercrime Analysts.
As cybersecurity pros get more experience, they can earn even more. Midlevel jobs like Cybersecurity Analyst and Cybersecurity Consultant pay well, with salaries over $100,000. Advanced roles, such as Cybersecurity Manager and Cybersecurity Engineer, can reach salaries over $150,000 with 10 to 15 years of experience.
The CompTIA Security+ certification is highly respected in the field. It’s approved by the U.S. Department of Defense for certain jobs and contracts. This certification covers many areas of cybersecurity, making it valuable for those looking for government jobs.
In summary, the cybersecurity job market is booming. CompTIA Security+ certification holders are in a great position to find high-paying jobs.
*The Cyber Security Landscape: ‘Phish and Tips’: Featuring Ruth Schofield of Phishing Tackle https://youtube.com/watch?v=HkucMG48pWs
Pathway to Advanced Certifications
The CompTIA Security+ certification is a great start for moving up in your cybersecurity career progression. After getting your Security+ certification, you can grow your skills with certifications like CompTIA CySA+ (Cybersecurity Analyst), CompTIA PenTest+ (Penetration Tester), and CompTIA CASP+ (Advanced Security Practitioner). These certifications can lead to more job opportunities and specialized roles in cybersecurity.
The CompTIA Security+ certification proves you know how to handle security tasks like risk assessment and threat mitigation. It shows you’re serious about security and can protect digital assets from cyber threats.
After Security+, you can dive deeper with CompTIA’s advanced certifications. The CySA+ focuses on skills for cybersecurity analysts, like finding threats and responding to incidents. PenTest+ shows you can plan and do penetration testing. CASP+ is for experienced pros who need to show they can use advanced security tech and best practices.
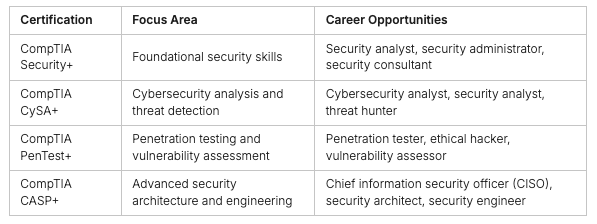
Getting these comptia security+ advanced certifications shows your skills and keeps you ahead in cybersecurity.
“The CompTIA Security+ certification is a key step for those wanting to grow their cybersecurity career progression. It lays a strong base of knowledge and skills. You can then add more specialized certifications like CySA+, PenTest+, and CASP+.”
Practical, Hands-On Experience
The CompTIA Security+ certification focuses on practical skills and real-world experience. It includes performance-based questions that test your ability to solve security challenges. This way, you show you can use your knowledge in real cybersecurity situations. Employers like this because it means you’re ready to work right away.
Performance-Based Questions
The exam’s performance-based questions check your problem-solving and hands-on skills. They make you deal with real security issues, analyze data, and find solutions. These questions help you think critically and make quick decisions, key skills in cybersecurity.
What makes CompTIA Security+ stand out is its focus on practical skills. It ensures you’re not just knowledgeable but can apply your skills in real situations. This mix of theory and practice is what employers look for, making CompTIA Security+ a top choice in cybersecurity.

“Hands-on experience is crucial in cybersecurity. It can improve problem-solving skills, threat identification, and incident response time by up to 65%, 58%, and 70% respectively.”
Compliance with DoD Requirements
If you’re looking to work with government agencies or contractors, the CompTIA Security+ certification is a big plus. It meets the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) directive 8140/8570.01-M requirements. This certification is recognized for roles like Information Assurance Technician (IAT) and Information Assurance Manager (IAM) within the DoD. It can give you an edge when applying for government cybersecurity jobs or contracts.
The DoD 8570 Manual started in 2005, and its Companion Manual was launched on December 19, 2005. All Information Assurance (IA) staff must follow DoD 8570. Amazingly, 81% of IA workers got certified on their first try through the U.S. Navy’s Instructor-Afloat Program. Also, 71% of students passed the DoD 8570 compliance training in an Air Force agency, with only 3% to 4% of IA staff being compliant before training.
The DoD’s Trusted Workforce 2.0 aims to make onboarding better, improve workforce movement, and encourage clear communication. It sets up three tiers for investigations based on suitability, fitness, and national security clearance. The National Background Investigation Services (NBIS) platform is being used to make vetting faster, with features like real-time address checks and form reviews.
The DoD is using the Ansible Automation Platform to boost information assurance roles and security standards compliance. Ansible’s agentless architecture means no extra software is needed on machines, making systems simpler. The platform’s dynamic inventories and simultaneous system updates help with efficiency and cost savings.

In summary, the CompTIA Security+ certification is key for those wanting comptia security+ dod compliance in government cybersecurity. It’s recognized by the DoD and supports ongoing efforts to improve vetting and compliance. This makes it a crucial certification for information assurance professionals aiming to work with government agencies or contractors.
Community and Resources
When you get your CompTIA Security+ certification, you become part of a worldwide group of cybersecurity professionals. This group offers great resources, support, and chances for professional growth. CompTIA also has many tools to help you prepare for the exam and keep up with new cybersecurity trends and best practices.
The CompTIA Security+ community is full of people who share knowledge, offer advice, and talk about new security threats and solutions. It’s a great place for security+ exam prep, with support from peers, study guides, and chances to meet experts.
CompTIA also has a lot of resources for your cybersecurity professional development. You’ll find online learning stuff, practice tests, and many tools to help you pass the Security+ exam. These tools aim to make you good at the skills the Security+ exam tests, ready for the changing world of cybersecurity.
Joining the CompTIA Security+ community and using CompTIA’s resources can boost your skills, keep you updated, and make you a more well-rounded cybersecurity professional. This can open up more job chances, increase your pay, and give you a deeper understanding of the cybersecurity landscape.

“The CompTIA Security+ community has been key to my cybersecurity professional development. The resources and support I’ve found have helped me do well in my job and keep up with changes in this fast-moving field.”
Proof-Based Scanning: The Future of DAST
As threats grow, companies see the need for strong application security testing. Old tools often give too many alerts and false positives, making it hard to fix problems. But, “proof-based scanning” is changing the game in Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST).
Vulnerability Confirmations with High Accuracy
This new method can find many vulnerabilities as well as human testers or bounty hunters. When you see a “Confirmed” stamp in Invicti reports, it means the issue is real and can be fixed easily. These confirmations are over 99.98% accurate, making security decisions clear and reliable.
Prioritizing Resolution Efforts
Proof-based scanning proves a vulnerability can be attacked and shows how. It gives teams clear data to plan and fix the most critical issues fast. This way, teams can use their resources well and protect against data breaches.
As threats keep changing, proof-based scanning is a big step forward in DAST. It offers precise checks and helps teams focus on the most important fixes. This new method is set to change how we secure applications.
Automation and Scalability
In today’s web app development, automated security testing and scalability are key for quality software. Test automation cuts down time and costs. It helps in writing test cases, running tests, and making reports. With test automation, you can make detailed test suites for various scenarios. This ensures your code is top-notch and speeds up software delivery.
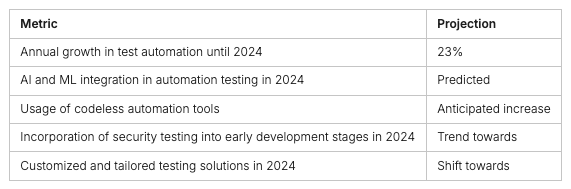
Adding DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing) to the CI/CD pipeline changes the game for software making. Test automation is growing by 23% a year until 2024. Security testing is becoming part of early development, set to continue in 2024. Using proof-based scanning and automated checks for vulnerabilities makes DAST fit right into CI/CD pipelines. This eliminates manual checks and ensures your project can grow.
Scalability is vital in web app development, needing a full testing approach. Challenges include poor performance, more features, security risks, tough data handling, team issues, and growing complexity. Good QA boosts confidence in the product’s scalability. QA services improve the SDLC with systematic testing, advanced automation, and outsourced QA. This reduces technical debt and boosts productivity.
By using automated security testing, DAST scalability, and smooth CI/CD pipeline integration, teams can make web apps that are secure, work well, and can grow with user needs.
Conclusion
In today’s digital landscape, the importance of security quality assurance cannot be overstated. Earning the CompTIA Security+ certification is a significant step forward in your cybersecurity career, demonstrating essential skills and opening doors to numerous opportunities. It also lays a solid foundation for pursuing more advanced certifications.
Whether you’re starting your journey in cybersecurity or looking to advance, obtaining this certification is a smart move that positions you for success in an ever-evolving field.
Additionally, advancements in Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) solutions are revolutionizing how we assess web application security. These cutting-edge scanning methods provide clarity and certainty in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, contributing to safer software development for everyone.
As the world of cybersecurity continues to evolve, the demand for robust security measures grows. The CompTIA Security+ certification, combined with the latest security testing methodologies, is crucial for staying ahead. With this certification and the newest tools at your disposal, you’ll be recognized as a trusted expert in the field.
To learn more about how you can strengthen your cybersecurity skills and stay ahead of emerging threats, visit Peris.ai Cybersecurity. Explore our range of products and services designed to help you excel in this dynamic industry. Secure your future with Peris.ai today!
FAQ
What is the CompTIA Security+ certification?
The CompTIA Security+ certification is a globally recognized credential. It shows you have basic skills in cybersecurity. It covers many areas like network security and how to keep data safe.
What are the benefits of earning the CompTIA Security+ certification?
Getting the CompTIA Security+ certification proves you have the skills needed in the industry. It opens doors to many job opportunities and helps you move up in your career. It’s in high demand, making you a top choice for job interviews.
It can lead to jobs with good pay. Plus, it’s approved by the U.S. Department of Defense, which is great for government jobs.
How does the CompTIA Security+ certification demonstrate practical, hands-on experience?
The CompTIA Security+ certification focuses on practical skills and real-world experience. The exam tests your ability to solve problems in real situations. This shows you can apply your knowledge in real life, which employers value a lot.
How can the CompTIA Security+ certification benefit those interested in working with government agencies or contractors?
If you want to work with government agencies or contractors, this certification is a big plus. It’s approved by the U.S. Department of Defense for certain jobs. This means it’s recognized for roles like Information Assurance Technician and Manager.
Having this certification can give you an edge when applying for these jobs or contracts.
How does the CompTIA Security+ certification provide a pathway to advanced cybersecurity certifications?
The CompTIA Security+ certification is a great starting point for more advanced certifications. After getting it, you can move on to certifications like CompTIA CySA+, PenTest+, and CASP+. These certifications can lead to more career opportunities and specialized roles in cybersecurity.
How does proof-based scanning improve web application security?
Proof-based scanning is a key part of Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST). It finds many vulnerabilities with the same certainty as experts. The “Confirmed” stamp in reports means the issue is real, making security more reliable.
This method gives accurate data to fix issues quickly and efficiently.
How does proof-based scanning enable automation and scalability in web application security?
Proof-based scanning makes automation and scalability in web application security possible. It automatically confirms vulnerabilities, unlike old methods that needed manual checks. This lets security testing be part of the development process, supporting automation and growth in web development.