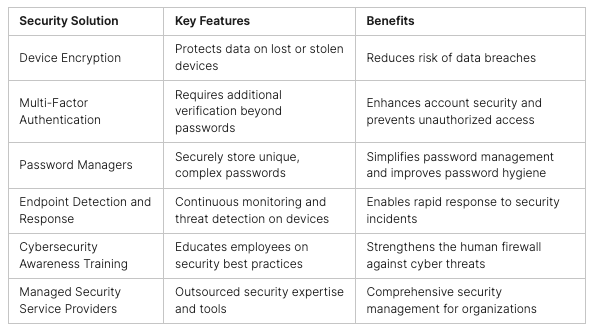
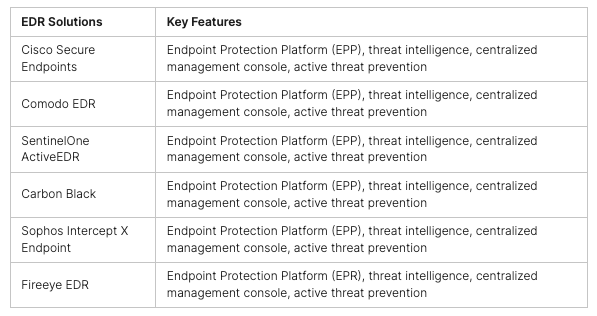
The digital world is changing fast, with more devices connected than ever. This includes not just computers and phones, but also smart devices and more. With more entry points for hackers, protecting these devices is key for businesses. Antivirus alone can’t keep up with today’s cyber threats.
This article looks at XDR (Extended Detection and Response) and EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response). We’ll see which one is better for keeping your business safe online. Knowing what each offers helps you choose the right cybersecurity for your company.
Key Takeaways
- More than 68% of organizations have been victims of endpoint threats.
- Remote workers account for 20% of security breaches in organizations.
- EDR focuses on protecting endpoints, offering visibility and threat prevention for individual devices.
- XDR provides a broader security approach by integrating security across various components.
- XDR complements EDR by incorporating telemetry from non-endpoint sources for enhanced security insights.
Differentiating EDR and XDR
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Explained
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a security tool that protects and watches over devices like computers and phones. It gathers data from these devices to find and fight off threats. This way, EDR helps keep devices safe by spotting and stopping threats early.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) Explained
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) looks at security from a bigger picture. It doesn’t just focus on devices but also on networks and cloud systems. This wide view helps XDR find threats more accurately and act faster, reducing mistakes.
XDR’s wide view helps fight threats better by understanding the whole security picture. It can also work together with other security areas to stop threats quickly.
Even though EDR and XDR share some features, they are different in what they do and how they do it. Companies need to think about their security needs and what they can do to choose the best option.

Both EDR and XDR need experts to set up and run well. They require knowledge of cyber threats and security. The right choice depends on what the company needs and what they can do.
EDR and XDR are key in keeping computers safe. For example, malware was behind up to 30% of data breaches in 2023, says Verizon. With more devices online, strong security is more important than ever.
Companies like WatchGuard offer tools like EDR and XDR to help fight threats. Their WatchGuard ThreatSync tool helps manage threats across different systems, making it easier to keep everything safe.
“XDR reduces manual investigation time, streamlines notifications, and cuts down on the volume of alerts.”
Importance of EDR and XDR in Cybersecurity
As more people work from home, the number of devices in organizations grows. Endpoint security strategies are now key. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions help monitor these devices. They detect and respond to security incidents.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) goes further. It combines data from various security products, like EDR, network, cloud, and email security.
XDR uses advanced analytics and machine learning to find and tackle threats. It automates incident response, making security operations better. Both EDR and XDR are vital for detecting and responding to threats. They improve incident response, reduce risk, and enhance security visibility.
EDR mainly focuses on endpoint security. XDR, on the other hand, looks at multiple data sources. It uses SIEM, UEBA, NDR, and EDR tools for a broader security view.
EDR uses signature-based detection and machine learning for endpoint security. XDR adds to this by analyzing network traffic, cloud services, and more.
EDR works with endpoint security tools and has some automation. XDR, however, works with the whole security stack. It offers advanced automation and orchestration across multiple security layers.
XDR quickly and accurately detects advanced attacks by analyzing various data sources. It provides a comprehensive security posture view for efficient threat detection and response. EDR protects against endpoint attacks. XDR, however, covers more sophisticated threats that traditional security measures can’t handle.

In summary, EDR and XDR are key to a strong cybersecurity strategy. They improve threat detection, incident response, risk reduction, and security visibility. EDR focuses on endpoint security. XDR’s comprehensive approach integrates data from multiple sources. This enables more efficient and effective security operations.
Key Differences Between EDR and XDR
Both Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) aim to boost cybersecurity. EDR mainly targets individual devices like laptops and servers. On the other hand, XDR uses data from many sources, including endpoints, networks, and cloud services.
Coverage
EDR and XDR differ in what they cover. EDR focuses on endpoint security, detecting and responding to threats on devices. XDR goes further, combining data from various tools for a broader security view.
- XDR offers wide security coverage, tackling threats on endpoints, networks, and clouds.
- XDR merges different security tools into one system, improving threat detection and response.
- EDR mainly deals with endpoint threats.
- XDR includes EDR and more, offering better protection across business systems.
XDR is a cost-effective option for businesses with many networks and cloud apps. It helps prevent costly breaches.
“XDR offers a centralized dashboard, enabling organizations to monitor and prioritize threat data from a single point.”
In summary, EDR and XDR differ mainly in their scope. EDR focuses on endpoint security, while XDR integrates data from various sources. This gives a complete view of an organization’s security and improves threat detection and response.
Detection and Response Capabilities
In today’s fast-changing cybersecurity world, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and Extended Detection and Response (XDR) are key. EDR uses methods like signature-based detection and machine learning to spot threats at endpoints. But, it might miss out on new, advanced attacks, leaving networks open to danger.
XDR goes beyond EDR by looking at more data, like network traffic and cloud services. This wider view helps XDR find threats that EDR might miss. Also, XDR can respond in more ways than just isolating endpoints or stopping processes.

The MITRE ATT&CK Framework is a key tool for EDR and XDR. It helps spot and understand adversary tactics. Using this framework, teams can better defend against threats, making their security stronger.
With cyber threats getting more complex, using advanced solutions like XDR is essential. XDR gives a full view of an organization’s security, helping teams fight threats better.

For those with limited resources or cybersecurity knowledge, Managed Detection and Response (MDR) is a good option. MDR combines EDR or XDR with expert security help, offering better threat detection and response.
As threats keep changing, it’s vital for businesses to use advanced security tools like EDR and XDR. These tools help teams detect and handle complex threats, protecting important assets and keeping businesses running.
XDR vs. EDR: Which Solution Best Protects Your Enterprise?
Enterprises today face many cyber threats. These threats target their endpoints, cloud, and mobile devices. The debate between EDR and XDR solutions is key in this digital world.
EDR gives deep insight into endpoints to prevent threats. XDR, on the other hand, offers security across endpoints, cloud, and mobile devices.
XDR makes security management simpler and enforces policies across an organization. Both EDR and XDR aim to stop threats before they happen. They use automated detection and response to lessen cyberattack impact.
EDR protects individual endpoints, while XDR covers multiple platforms. XDR also integrates threat management in one solution, making security operations smoother.
Choosing between EDR and XDR is key for endpoint security. XDR is the next step in endpoint security, offering advanced threat protection. It’s best for modern computing, distributed workforces, and diverse endpoint usage.
“XDR coordinates and extends the value of siloed security tools, unifying and streamlining security analysis, investigation, and remediation into one consolidated console.”
Choosing between EDR and XDR depends on your enterprise’s needs. Knowing each solution’s strengths and weaknesses helps protect your digital assets and infrastructure.
Pros and Cons of EDR
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions protect against threats at the endpoint level. They offer real-time monitoring, threat detection, and incident response. EDR’s main benefits include analyzing a lot of data to find malicious activities and quickly stopping security breaches.
However, EDR only protects endpoints and might miss threats that spread across the IT environment.
One big plus of EDR is its ability to do detailed forensic analysis. This helps organizations understand security incidents and find their causes. Also, EDR is often cheaper than Extended Detection and Response (XDR), which is good for businesses with tight budgets.
But, EDR’s main weakness is its use of signature-based detection. This method doesn’t work well against unknown or zero-day threats. Also, the cost of a data breach can be very high, averaging $4.34 million, as reported by Xcitium.
Choosing between EDR and XDR depends on what a company needs, its resources, and its current setup. EDR gives focused security, quick response, and deep insight into endpoint activities. XDR offers wide visibility, automated threat detection, and easier security management. Companies need to think about these points to pick the right cybersecurity solution for them.
Integration and Automation
Organizations are looking to boost their cybersecurity by integrating and automating security solutions. EDR, or Endpoint Detection and Response, works with other endpoint security tools. It also connects with network security tools to give a full view of attacks. On the other hand, XDR, or Extended Detection and Response, integrates with many security tools. This includes network, identity, cloud, and email security.
EDR automates common actions like isolating endpoints and stopping processes. XDR, with SOAR, offers advanced automation and orchestration. It works across multiple security layers, automating complex workflows. This makes it easier to detect, analyze, and respond to threats. SIEM and SOAR systems are key in improving these abilities.
Automation and Orchestration
Automation and orchestration are vital in cybersecurity. SOAR technology automates responses and supports multiple vendors. It makes incident response tasks easier and automates security operations. MDR services combine tech and human expertise to fight cyber threats, boosting security.
Combining EDR, XDR, and SOAR offers a strong security strategy. EDR targets endpoint threats, while XDR covers more areas. With SOAR, these tools automate complex workflows. This helps organizations respond to threats more efficiently.
The need to integrate security tools and automate workflows is growing. Using EDR, XDR, and SOAR, organizations can improve their security. They can better defend against various cyber threats.
Conclusion
In today’s complex cybersecurity landscape, proactive and adaptive protection across endpoints, networks, and beyond is essential. Brahma’s comprehensive EDR/NDR/XDR platform equips organizations with powerful, enterprise-grade tools to detect, prevent, and respond to threats at every level. By combining advanced machine learning with behavior analytics, Brahma ensures both known and emerging threats are swiftly identified, mitigated, and managed.
Whether focused on in-depth endpoint protection through EDR or a broader security strategy via XDR, Brahma offers a tailored approach to meet your organization’s unique needs. With real-time dashboard monitoring, MITRE ATT&CK framework coverage, and an intuitive vulnerabilities dashboard, Brahma brings clarity, agility, and strength to your security operations.
Strengthen your cybersecurity with Brahma. Discover more about our advanced solutions and how we can empower your organization’s digital defense—visit Peris.ai today.
FAQ
What is the difference between XDR and EDR?
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) mainly deals with endpoint security. It gives visibility and control over devices like desktops and laptops. XDR (Extended Detection and Response) looks at the bigger picture. It gives security teams a full view of the company’s security to make quicker and smarter decisions.
What are the key capabilities of EDR and XDR?
EDR uses methods like signature-based detection and machine learning to find threats at the endpoint. XDR goes further by looking at network traffic, cloud services, and more. This helps it spot complex threats that EDR might miss.
What are the advantages of XDR over EDR?
XDR can look at data from many places, like networks and clouds. This lets it find unusual behaviors and complex attacks that EDR might not see. XDR’s detailed view and advanced analytics make it better for protecting a company’s digital world.
How do EDR and XDR integrate with other security tools?
EDR works with other endpoint security tools and can link with network security tools too. XDR is made to work with many security tools, including network, cloud, and email security.
What are the automation and orchestration capabilities of EDR and XDR?
EDR automates simple actions like isolating endpoints. XDR, with a SOAR solution, can automate more complex tasks. It works across different security layers, making complex responses easier for teams.